Introduction: Why Melasma Requires a Precision-Based Approach in Abu Dhabi
Melasma is one of the most persistent and emotionally challenging pigmentation concerns, especially for patients living in sun-intense climates like Abu Dhabi. The combination of UV exposure, heat-induced inflammation, hormonal changes, and genetic predisposition makes pigmentation recurrence a constant possibility if treatment is not carefully managed. Dermatologist Abu Dhabi specialists recognize melasma as a chronic pigmentary disorder, something that cannot be erased overnight but can be strategically controlled, faded, and stabilized through a multi-layered plan. The modern philosophy here rejects outdated, overly aggressive treatments that cause rebound pigmentation and instead embraces progressive protocols that respect the integrity of the skin barrier. Patients today are not simply looking for short-term lightning. They want long-term clarity, reduced relapse, and a complexion that maintains even tone regardless of seasonal changes. This shift has given rise to advanced melasma treatment plans that combine precision lasers, pharmacological interventions, and dermal repair strategies tailored to individual skin types.
Understanding Melasma Biology: Why Underground Triggers Must Be Treated First
To treat melasma effectively, dermatologists begin by understanding its origin at a cellular level. Melasma is driven by melanocyte overstimulation, which responds aggressively to heat, sunlight, hormones, and inflammation. This makes melasma fundamentally different from surface-level pigmentation like acne marks or sunspots. The pigment sits deeper, often in the dermal layers, and that is why superficial chemical peels or basic brightening creams fail to achieve sustained improvement. Dermatologists in Abu Dhabi examine the depth of pigment using tools like Wood’s lamp imaging and dermoscopy to categorize melasma as epidermal, dermal, or mixed. The sensitivity of melanocytes also matters: some individuals experience flare-ups even after minor sun exposure or heat from cooking. Recognizing these patterns allows clinicians to craft treatment plans that begin with stabilization before brightening. The foundational phase may include barrier repair creams, anti-inflammatory topicals, and pigment regulators to calm the melanocytes before introducing lasers or chemical resurfacing. This biology-based sequencing prevents rebound pigmentation and preserves the long-term health of the skin.
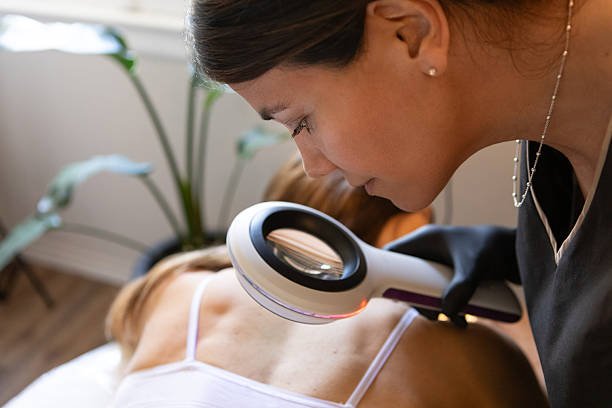
Laser Therapies: Precision Technology as the Core of Modern Melasma Correction
Abu Dhabi dermatologists rely on a new generation of laser systems engineered for pigment control rather than brute-force removal. Devices like Q-switched lasers, Picosecond platforms, and fractional non-ablative systems allow physicians to reach pigment clusters without overheating the surrounding tissue. Unlike aggressive treatments of the past, which sometimes triggered darker regrowth, today’s methods use controlled energy to break apart pigment particles while safeguarding the skin barrier. Picosecond lasers are particularly beneficial for deeper melasma patterns because they use ultra-short pulses to fragment melanized particles into microscopic debris that the immune system gradually clears. Fractional lasers, meanwhile, resurface the epidermis and encourage collagen remodeling, improving texture and clarity. Some dermatologists alternate between these technologies across multiple sessions to avoid overwhelming the skin. Cooling devices, gentle mode calibrations, and spacing sessions several weeks apart are common strategies that ensure the inflammation threshold is never exceeded. This precision-based laser philosophy allows melasma to fade gradually, safely, and with higher resistance to recurrence.
Pharmacological Care: Medication-Driven Intervention for Melanocyte Regulation
Dermatologists in Abu Dhabi rely heavily on pharmacological tools to suppress melanocyte activity and break pigment production cycles. Hydroquinone remains a cornerstone medication when used correctly in controlled, time-limited intervals to avoid irritation and resistance. In many cases, it is combined with retinoids and mild corticosteroids, forming what is often referred to as a triple combination protocol. These formulations accelerate cell turnover, reduce inflammation, and prevent new pigment from forming. However, pharmaceutical care is no longer limited to this traditional combination. Newer topical agents like tranexamic acid have emerged as key players for hormonal melasma and vascular pigment triggers. Niacinamide reduces inflammatory stress on pigment cells, azelaic acid supports epidermal regeneration, and cysteamine offers brightening benefits without compromising skin sensitivity. Dermatologists now build medication timelines where products rotate seasonally or according to treatment milestones. This avoids tolerance buildup and keeps melanocytes responsive to therapy. These pharmacological plans are never generic; they are layered, reviewed, and recalibrated as the skin evolves.
Chemical Peels and Controlled Exfoliation to Support Pigment Lift
Chemical peels have an important role in melasma treatment, but they must be chosen strategically. Dermatologists in Abu Dhabi are selective about formulas, avoiding deep or overly harsh peels that might cause post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Instead, they rely on controlled exfoliation with compounds like mandelic acid, lactic acid, azelaic acid, and low-strength TCA blends. These formulas loosen epidermal pigment, refine texture, and prepare the skin for laser absorption. Peels are often scheduled between laser sessions to maximize clarity without overwhelming the skin. In some protocols, dermatologists integrate peel series with tranexamic acid infusions or topical brightening ampoules, giving the skin both exfoliation and stabilization in one visit. The strategy here is not to strip the skin, but to gradually diminish pigmentation while maintaining barrier integrity. When patients follow aftercare diligently including hydration, gentle cleansers, and strict sun protection the results compound over time.
Barrier Repair and Melanocyte Stabilization: Why Maintenance Determines Success
Melasma treatment does not end the moment pigment fades; the maintenance phase is often considered the most important stage. Dermatologists in Abu Dhabi focus intensely on barrier repair as a defense mechanism, because a damaged skin barrier allows inflammation and UV penetration to reignite melanocyte activity. Medical-grade moisturizers rich in ceramides, cholesterol, and fatty acids are commonly recommended to reinforce the epidermis. Antioxidants such as vitamin C, resveratrol, and ferulic acid reduce oxidative stress, while peptides help rebuild the dermal structure that supports tone uniformity. Maintenance might also include intermittent LED therapy to calm inflammation and restore energy balance to the skin. This holistic approach shifts melasma treatment from reactive to preventive. By strengthening the barrier and stabilizing pigment signals, dermatologists create a biological environment where melasma struggles to return.
Sun Protection and Heat Management in a GCC Climate
In Abu Dhabi, sun exposure is not merely an environmental factor, it is the defining variable in melasma management. Long-term success depends on strict photoprotection habits that go beyond basic sunscreen application. Dermatologists emphasize broad-spectrum formulas with mineral filters such as zinc oxide and titanium dioxide, which reflect UV rather than absorb it. These are often preferred for sensitive melasma-prone skin because they produce less heat. Sunscreens may also include iron oxides for visible light protection, which is crucial for patients experiencing pigment activation from indoor lighting or device screens. Heat management is equally important; patients are advised to avoid peak UV hours, apply cold compresses post-laser, and minimize prolonged heat exposure from saunas or high-temperature cooking environments. When patients integrate these practices consistently, laser and pharmacological progress is preserved rather than undone.
Cultural Sensitivity and Customized Care for Abu Dhabi’s Diverse Population
Abu Dhabi’s dermatology landscape treats a wide range of skin tones, ethnic backgrounds, and genetic pigment responses. Fitzpatrick skin types III to VI often present elevated melanin reactivity, requiring gentler laser settings and conservative peel formulations. Dermatologists are trained to assess how each skin tone metabolizes treatment energy and medication strength. For many women dealing with melasma caused or worsened by pregnancy, postpartum hormonal changes, or contraceptive adjustments, treatment plans are modified with safety and gentleness in mind. Patients wearing hijab may face friction and heat-trap pigmentation along the forehead and hairline, which must be treated through barrier repair and pigment inhibition. These personalized considerations ensure that melasma treatment in Abu Dhabi is never one-size-fits-all.
Long-Term Expectations and Psychological Relief Through Clarity and Stability
Melasma can significantly impact confidence, especially when patients feel trapped in a cycle of fading and returning pigment. Dermatologists in Abu Dhabi focus on providing predictability and transparency throughout the journey. Patients are guided to understand that melasma is manageable but not curable, and that success lies in consistent habits, not sudden transformations. This mindset shift helps patients feel in control rather than discouraged by the chronic nature of their condition. When pigment softens, texture evens, and skin tone brightens gradually, the emotional relief is profound. The ultimate goal is not perfection but long-term clarity, reduced triggers, and the confidence of knowing flare-ups can be controlled.
Conclusion
Melasma treatment in Abu Dhabi is evolving into a sophisticated medical strategy supported by lasers, pharmaceuticals, dermal repair, and lifestyle adjustments tailored to the GCC climate. Dermatologists no longer chase quick fixes; they build structured plans that respect the biology of melanocytes and the psychological needs of patients. With each advancement in laser precision, pigment-modulating medication, and inflammation control, the possibility of stable, long-lasting clarity becomes more realistic. In this environment, melasma is no longer a lifelong frustration but a condition that can be intelligently managed, allowing patients to reclaim confidence in their skin and appearance.